Wordscores
Wordscores is a scaling model for estimating the positions (mostly of political actors) for dimensions that are specified a priori. Wordscores was introduced in Laver, Benoit and Garry (2003) and is widely used among political scientists.
require(quanteda)
require(quanteda.textmodels)
require(quanteda.textplots)
require(quanteda.corpora)
Training a Wordscores model requires reference scores for texts whose policy positions on well-defined a priori dimensions are “known”. Afterwards, Wordscores estimates the positions for the remaining “virgin” texts.
In this example, we will use manifestos of the 2013 and 2017 German federal elections. For the 2013 elections we will assign the average expert evaluations from the 2014 Chapel Hill Expert Survey for the five major parties in order to predict the party positions for the 2017 manifestos.
corp_ger <- download(url = "https://www.dropbox.com/s/uysdoep4unfz3zp/data_corpus_germanifestos.rds?dl=1")
summary(corp_ger)
## Corpus consisting of 12 documents, showing 12 documents:
##
## Text Types Tokens Sentences year party ref_score
## AfD 2013 450 944 43 2013 AfD NA
## CDU-CSU 2013 7615 46535 2527 2013 CDU-CSU 5.92
## FDP 2013 7953 42298 2375 2013 FDP 6.53
## Gruene 2013 13839 93595 5126 2013 Gruene 3.61
## Linke 2013 8451 43382 1850 2013 Linke 1.23
## SPD 2013 8360 47348 2532 2013 SPD 3.76
## AfD 2017 5947 18754 715 2017 AfD NA
## CDU-CSU 2017 4890 21510 1256 2017 CDU-CSU NA
## FDP 2017 8676 37609 1925 2017 FDP NA
## Gruene 2017 13353 72645 3220 2017 Gruene NA
## Linke 2017 11830 65728 2755 2017 Linke NA
## SPD 2017 8400 41938 2401 2017 SPD NA
Now we can apply the Wordscores algorithm to a document-feature matrix.
# tokenize texts
toks_ger <- tokens(corp_ger, remove_punct = TRUE)
# create a document-feature matrix
dfmat_ger <- dfm(toks_ger) %>%
dfm_remove(pattern = stopwords("de"))
# apply Wordscores algorithm to document-feature matrix
tmod_ws <- textmodel_wordscores(dfmat_ger, y = corp_ger$ref_score, smooth = 1)
summary(tmod_ws)
##
## Call:
## textmodel_wordscores.dfm(x = dfmat_ger, y = corp_ger$ref_score,
## smooth = 1)
##
## Reference Document Statistics:
## score total min max mean median
## AfD 2013 NA 455 0 23 0.01093 0
## CDU-CSU 2013 5.92 23060 0 245 0.55373 0
## FDP 2013 6.53 20603 0 186 0.49473 0
## Gruene 2013 3.61 45759 0 398 1.09879 0
## Linke 2013 1.23 21011 0 234 0.50453 0
## SPD 2013 3.76 23150 0 214 0.55589 0
## AfD 2017 NA 9899 0 108 0.23770 0
## CDU-CSU 2017 NA 10753 0 136 0.25821 0
## FDP 2017 NA 19358 0 261 0.46483 0
## Gruene 2017 NA 40982 0 1086 0.98408 0
## Linke 2017 NA 33347 0 788 0.80074 0
## SPD 2017 NA 20836 0 186 0.50032 0
##
## Wordscores:
## (showing first 30 elements)
## alternative deutschland wahlprogramm
## 3.291 4.741 3.296
## währungspolitik fordern geordnete
## 4.530 3.255 4.241
## auflösung euro-währungsgebietes braucht
## 3.337 4.241 4.153
## euro ländern schadet
## 3.329 4.227 3.912
## wiedereinführung nationaler währungen
## 4.464 4.578 4.241
## schaffung kleinerer stabilerer
## 4.289 4.426 4.241
## währungsverbünde dm darf
## 4.241 4.241 3.871
## tabu änderung europäischen
## 4.159 4.227 4.359
## verträge staat ausscheiden
## 3.553 4.792 3.698
## ermöglichen volk demokratisch
## 4.355 4.241 2.271
Next, we will predict the Wordscores for the unknown virgin texts.
pred_ws <- predict(tmod_ws, se.fit = TRUE, newdata = dfmat_ger)
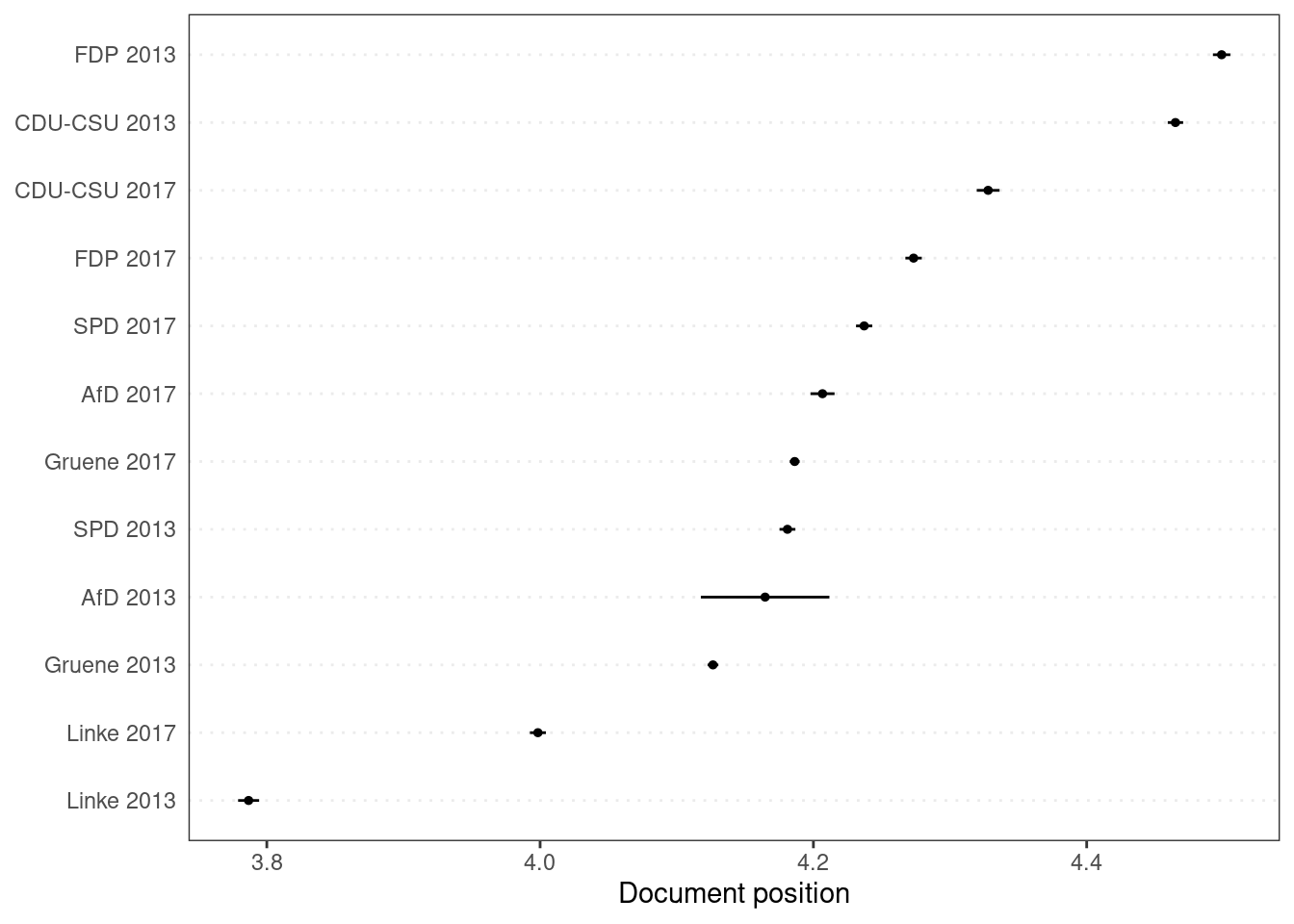
Finally, we can plot the fitted scaling model using quanteda‘s textplot_scale1d() function.
textplot_scale1d(pred_ws)
- Laver, Michael, Kenneth R Benoit, and John Garry. 2003. “Extracting Policy Positions From Political Texts Using Words as Data.” American Political Science Review 97(2): 311-331.
- Lowe, Will. 2008. “Understanding Wordscores.” Political Analysis 16(4): 356-371.